
The modern supply chain faces unprecedented challenges and opportunities. Globalization, fluctuating demand, and increasing customer expectations necessitate a fundamental shift towards greater efficiency and resilience. Digital transformation offers a powerful solution, leveraging cutting-edge technologies to streamline operations, enhance visibility, and foster collaboration across the entire supply chain ecosystem. This exploration delves into the multifaceted impact of digital technologies, examining their applications, benefits, and challenges within the context of modern supply chain management.
From the integration of Internet of Things (IoT) devices for real-time tracking to the application of artificial intelligence (AI) for predictive analytics, the potential for optimization is vast. This analysis will unpack the key technological drivers, their implementation strategies, and the resulting improvements in areas such as procurement, inventory management, logistics, and risk mitigation. Ultimately, we will examine how digital transformation is shaping the future of supply chain operations, fostering greater agility, responsiveness, and sustainability.
Defining Digital Transformation in Supply Chain
Digital transformation in supply chain management signifies a fundamental shift from traditional, often siloed, processes to a more integrated and data-driven approach. This involves leveraging technologies like artificial intelligence, machine learning, the Internet of Things (IoT), blockchain, and advanced analytics to optimize every stage of the supply chain, from procurement and production to logistics and delivery. The ultimate goal is to enhance efficiency, improve visibility, increase agility, and ultimately boost profitability.Digital transformation isn’t merely about adopting new technologies; it’s about fundamentally rethinking how the entire supply chain operates and integrating technology seamlessly to achieve strategic business objectives.
This requires a holistic approach that encompasses people, processes, and technology, fostering a culture of innovation and continuous improvement.
Key Drivers and Motivations for Digital Adoption in Supply Chains
Several factors are driving the widespread adoption of digital technologies within supply chains. Increasing global competition necessitates enhanced efficiency and responsiveness to meet ever-changing customer demands. The need for greater transparency and traceability throughout the supply chain, particularly in response to consumer concerns about sustainability and ethical sourcing, is also a significant motivator. Furthermore, the sheer volume of data generated across the supply chain presents an opportunity to extract valuable insights for improved decision-making.
Cost reduction, risk mitigation, and improved customer satisfaction are additional key drivers. For example, real-time tracking of shipments via IoT devices allows for proactive intervention in case of delays, minimizing disruptions and associated costs.
Comparison of Traditional and Digitally Transformed Supply Chains
Traditional supply chain models are often characterized by manual processes, limited visibility, and reactive decision-making. Information flows are slow and fragmented, leading to inefficiencies and delays. In contrast, digitally transformed supply chains leverage data analytics to gain real-time visibility into every aspect of the operation. This enables proactive decision-making, optimized inventory management, and improved responsiveness to market changes.
For instance, a traditional supply chain might rely on periodic inventory checks, potentially leading to stockouts or overstocking. A digitally transformed supply chain, using sensors and real-time data analysis, can automatically adjust inventory levels based on actual demand, preventing these issues. The key difference lies in the level of automation, integration, and data-driven decision-making. Digitally transformed supply chains are significantly more efficient and effective, leading to reduced costs, improved customer satisfaction, and a stronger competitive advantage.
Consider Amazon’s fulfillment network as a prime example of a highly digitally transformed supply chain, utilizing sophisticated algorithms and robotics to optimize warehousing, picking, and delivery.
Technologies Enabling Digital Transformation
Digital transformation in supply chains relies heavily on the integration of advanced technologies. These technologies, when implemented strategically, can significantly improve efficiency, visibility, and responsiveness across the entire supply chain network. Their combined power allows for a more agile, data-driven, and ultimately, profitable operation.
Several key technologies are driving this transformation, each offering unique capabilities and addressing specific challenges. Understanding their functionalities and limitations is crucial for successful implementation.
Specific Technologies and Their Applications
The following technologies are instrumental in driving digital transformation within supply chain management. Their application varies depending on the specific needs and goals of the organization, but their collective impact is undeniable.
| Technology | Application | Benefits | Challenges |
|---|---|---|---|
| Internet of Things (IoT) | Real-time tracking of goods, predictive maintenance of equipment, monitoring environmental conditions during transport. | Enhanced visibility, improved efficiency, reduced waste, proactive problem-solving. | Data security concerns, integration complexities, high initial investment costs. |
| Artificial Intelligence (AI) | Demand forecasting, route optimization, fraud detection, predictive analytics for inventory management. | Improved accuracy in forecasting, optimized resource allocation, reduced operational costs, enhanced decision-making. | Data bias issues, lack of skilled workforce, high implementation costs, ethical considerations. |
| Blockchain | Secure and transparent tracking of goods, improved traceability, enhanced supply chain security, streamlined documentation processes. | Increased transparency and accountability, reduced counterfeiting, improved trust among stakeholders, faster transaction processing. | Scalability limitations, regulatory uncertainties, technological complexity, interoperability issues. |
| Cloud Computing | Data storage and management, software deployment, collaborative platforms, enhanced scalability and flexibility. | Reduced IT infrastructure costs, improved accessibility, increased scalability, enhanced collaboration. | Data security and privacy concerns, vendor lock-in, dependency on internet connectivity, potential for data breaches. |
Risks and Challenges of Technology Implementation
While the benefits of digital transformation are substantial, several risks and challenges must be considered for successful implementation. Careful planning, robust risk mitigation strategies, and ongoing monitoring are essential to navigate these complexities.
- High initial investment costs: Implementing new technologies often requires significant upfront investment in hardware, software, and skilled personnel.
- Data security and privacy concerns: The increased reliance on data raises concerns about security breaches and the protection of sensitive information.
- Integration complexities: Integrating new technologies with existing systems can be complex and time-consuming, requiring careful planning and coordination.
- Lack of skilled workforce: Successfully implementing and managing these technologies requires a workforce with the necessary skills and expertise.
- Resistance to change: Employees may resist adopting new technologies, requiring effective change management strategies.
- Vendor lock-in: Choosing a specific technology provider can lead to vendor lock-in, limiting flexibility and options in the future.
- Regulatory compliance: Adherence to data privacy regulations and other relevant laws is crucial.
Impact on Supply Chain Processes
Digital transformation is profoundly reshaping supply chain processes, driving efficiency, transparency, and responsiveness across the board. The integration of advanced technologies is streamlining operations, reducing costs, and improving overall agility, allowing businesses to better adapt to the ever-changing demands of the global market. This section will explore the impact of digital transformation on key supply chain processes.
The implementation of digital technologies has led to significant improvements in various aspects of supply chain management. From procurement to final delivery, companies are leveraging data analytics, automation, and connectivity to optimize their operations and enhance customer satisfaction. The resulting gains in efficiency and visibility translate to reduced costs, improved inventory control, and faster response times to market fluctuations.
Procurement Process Improvements
Digital technologies have revolutionized procurement, moving it from a largely manual and paper-based system to a streamlined, automated process. This involves using e-procurement platforms, which automate purchase orders, invoice processing, and supplier communication. Real-time data analysis allows for better negotiation with suppliers and the identification of cost savings opportunities.
- Automated Purchase Order Generation: E-procurement systems automatically generate purchase orders based on pre-defined parameters, reducing manual effort and errors.
- Improved Supplier Relationship Management: Digital platforms facilitate seamless communication and collaboration with suppliers, leading to stronger relationships and better negotiation outcomes.
- Enhanced Spend Visibility: Real-time data analytics provides complete visibility into procurement spend, allowing for better cost control and identification of areas for optimization.
Inventory Management Enhancements
Digital transformation is optimizing inventory management through real-time visibility and predictive analytics. Technologies like RFID and IoT sensors provide accurate and up-to-the-minute data on inventory levels, enabling businesses to make informed decisions about ordering, storage, and allocation. This minimizes stockouts and overstocking, reducing costs and improving customer service.
- Real-time Inventory Tracking: RFID tags and IoT sensors provide accurate and real-time data on inventory levels, location, and movement.
- Demand Forecasting: Advanced analytics and machine learning algorithms predict future demand, enabling businesses to optimize inventory levels and avoid stockouts or overstocking.
- Improved Warehouse Management: Automated guided vehicles (AGVs) and warehouse management systems (WMS) streamline warehouse operations, increasing efficiency and reducing errors.
Logistics and Delivery Optimization
Digital technologies are transforming logistics and delivery by improving route optimization, real-time tracking, and last-mile delivery efficiency. GPS tracking, route planning software, and delivery management systems provide greater visibility and control over the entire delivery process. This leads to faster delivery times, reduced transportation costs, and improved customer satisfaction.
- Route Optimization: Advanced algorithms optimize delivery routes, reducing transportation costs and delivery times.
- Real-time Tracking and Visibility: GPS tracking provides real-time visibility into the location and status of shipments, allowing for proactive issue resolution.
- Improved Last-Mile Delivery: Delivery management systems and technologies like drones and autonomous vehicles are improving the efficiency and speed of last-mile delivery.
Supply Chain Visibility and Collaboration
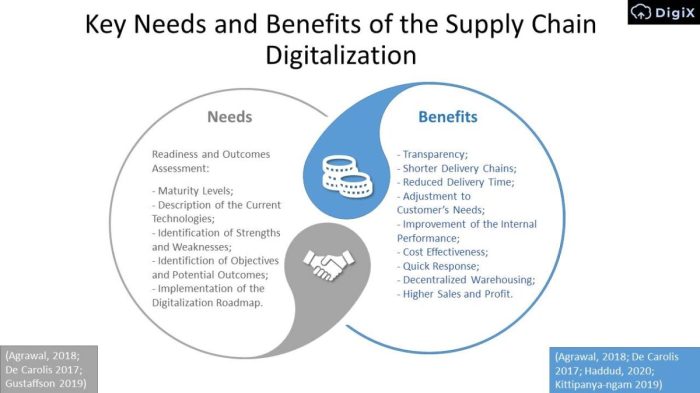
Digital transformation fundamentally alters supply chain visibility and collaboration, moving away from fragmented, siloed systems towards a unified, interconnected network. This enhanced transparency and streamlined communication significantly improve efficiency, responsiveness, and overall supply chain resilience.Digital technologies provide a real-time, holistic view of the entire supply chain, from the sourcing of raw materials to the delivery of finished goods to the end consumer.
This comprehensive visibility allows businesses to identify bottlenecks, predict potential disruptions, and proactively mitigate risks, ultimately leading to improved operational efficiency and reduced costs.
Enhanced Visibility Across the Supply Chain
The implementation of technologies like RFID, IoT sensors, and blockchain creates a digital thread that tracks goods and materials throughout their journey. Real-time data capture and analysis provide accurate, up-to-the-minute information on inventory levels, location of goods, and transportation status. This contrasts sharply with traditional methods relying on manual data entry and infrequent updates, which often resulted in inaccurate information and delays.
For example, a manufacturer can track the exact location of their components in real-time, knowing precisely when they are expected to arrive at the factory, enabling better production planning and minimizing downtime. Similarly, retailers can monitor inventory levels across their distribution network, ensuring that shelves are always stocked with the right products at the right time.
Improved Collaboration Among Supply Chain Partners
Improved visibility fosters stronger collaboration among all stakeholders. Shared platforms and data-driven insights enable seamless information exchange between suppliers, manufacturers, distributors, and retailers. This collaborative environment allows for proactive problem-solving, optimized resource allocation, and improved responsiveness to market changes. For instance, if a supplier experiences a delay, the information is instantly shared with the manufacturer, who can then adjust production schedules accordingly, preventing cascading disruptions down the supply chain.
This collaborative approach reduces the likelihood of stockouts, minimizes waste, and strengthens relationships between supply chain partners.
Scenario: Enhanced Collaboration through Digital Tools
Imagine a global apparel company using a cloud-based platform to manage its supply chain. This platform integrates data from various sources, including suppliers’ production schedules, shipping information, and retailer sales data. When a sudden surge in demand for a particular item occurs, the platform automatically alerts the manufacturer, who can then increase production accordingly. Simultaneously, the platform optimizes transportation routes and schedules to ensure timely delivery to retailers.
The platform also facilitates communication between all stakeholders, enabling them to collaboratively address any potential challenges. This integrated approach minimizes disruptions, ensures efficient resource allocation, and improves customer satisfaction. The result is a more agile and responsive supply chain that can quickly adapt to changing market conditions.
Data Analytics and Decision-Making
Data analytics plays a pivotal role in transforming supply chain management from a reactive to a proactive function. By leveraging the vast amounts of data generated throughout the supply chain, businesses can gain actionable insights that optimize operations, enhance efficiency, and improve overall profitability. This shift towards data-driven decision-making allows for more informed choices, leading to better outcomes across various aspects of the supply chain.The power of data analytics lies in its ability to uncover hidden patterns and trends that would otherwise remain unnoticed.
This allows for a more precise understanding of customer demand, supplier performance, and inventory levels. Through sophisticated algorithms and predictive modeling, businesses can anticipate potential disruptions and proactively implement mitigation strategies. This proactive approach significantly reduces the impact of unforeseen events and strengthens the overall resilience of the supply chain.
Optimizing Inventory Levels with Data Analytics
Effective inventory management is crucial for maintaining a balance between meeting customer demand and minimizing storage costs. Data analytics provides the tools to achieve this delicate balance. By analyzing historical sales data, seasonality patterns, and external factors such as economic indicators, businesses can forecast demand with greater accuracy. This precise forecasting allows for optimized inventory levels, reducing the risk of stockouts (leading to lost sales and customer dissatisfaction) and overstocking (resulting in excess holding costs and potential obsolescence).
For example, a retailer using predictive analytics might anticipate a surge in demand for a specific product during a holiday season and adjust their inventory accordingly, ensuring sufficient stock to meet the increased demand without incurring excessive holding costs.
Predicting Demand and Improving Forecasting Accuracy
Accurate demand forecasting is the cornerstone of effective supply chain planning. Data analytics enhances forecasting accuracy by incorporating a wider range of data sources and employing advanced statistical models. Factors such as weather patterns, social media trends, economic indicators, and even competitor activity can be integrated into predictive models to create more comprehensive and accurate forecasts. For instance, a food manufacturer might use data analytics to predict fluctuations in demand based on seasonal changes in consumer preferences, enabling them to adjust production schedules and resource allocation accordingly.
This proactive approach prevents production bottlenecks and ensures timely delivery to meet customer needs.
Mitigating Supply Chain Risks Through Data-Driven Insights
Supply chains are inherently susceptible to various risks, including disruptions caused by natural disasters, geopolitical instability, and supplier failures. Data analytics helps mitigate these risks by providing early warning signals and enabling proactive responses. By monitoring real-time data on supplier performance, transportation routes, and inventory levels, businesses can identify potential bottlenecks or disruptions before they escalate into major problems. For example, a company might use data analytics to detect a potential delay in the delivery of raw materials from a specific supplier due to a reported port congestion.
This early warning allows the company to explore alternative sourcing options or adjust production schedules to avoid a significant disruption in their supply chain.
Hypothetical Scenario: Preventing a Major Supply Chain Disruption
Imagine a global manufacturer of electronics components experiencing a sudden and unexpected surge in demand for a specific chip used in their flagship product. Traditional forecasting methods might fail to predict this spike accurately, leading to potential stockouts and production delays. However, by employing data analytics, specifically incorporating real-time sales data, social media sentiment analysis (detecting increased online buzz about the product), and competitor activity monitoring, the company could detect this demand surge early on.
This early detection would allow the company to proactively increase production, secure additional chip supplies from alternative suppliers, and adjust logistics to ensure timely delivery of the finished product. This proactive approach, enabled by data analytics, would prevent a major supply chain disruption, avoiding significant financial losses and reputational damage.
Supply Chain Resilience and Risk Management

Digital transformation is no longer a luxury but a necessity for supply chains seeking to thrive in today’s volatile global landscape. By leveraging advanced technologies, businesses can build significantly more resilient and adaptable supply chains, capable of weathering unforeseen disruptions and emerging threats. This enhanced resilience translates directly into improved profitability, reduced operational costs, and a stronger competitive advantage.Digital technologies offer a powerful toolkit for mitigating a wide range of supply chain risks.
These technologies provide the means to proactively identify potential vulnerabilities, monitor real-time performance, and respond swiftly and effectively to disruptions, ultimately minimizing their impact on the business. This proactive approach stands in stark contrast to traditional reactive strategies, which often result in significant financial losses and reputational damage.
Enhanced Visibility and Predictive Analytics for Risk Mitigation
Real-time visibility into the entire supply chain, provided by technologies such as IoT sensors, RFID tracking, and blockchain, allows businesses to anticipate potential disruptions before they materialize. This proactive monitoring enables early identification of bottlenecks, delays, or potential quality issues. Furthermore, advanced analytics tools can process vast quantities of data to identify patterns and predict potential risks with greater accuracy.
For instance, machine learning algorithms can analyze historical data on weather patterns, geopolitical events, and transportation delays to forecast the probability of future disruptions, allowing businesses to implement preventative measures. This predictive capability allows for more agile responses and optimized resource allocation, reducing the overall impact of potential disruptions.
Digital Technologies Mitigating Specific Supply Chain Risks
Digital transformation offers specific solutions for a range of supply chain risks. For example, blockchain technology enhances transparency and traceability, reducing the risk of counterfeiting and fraud. Advanced analytics can help optimize inventory levels, minimizing the risk of stockouts or excess inventory. Robust cybersecurity measures, including encryption and multi-factor authentication, protect sensitive data from breaches and cyberattacks.
Finally, digital twin technology allows for the simulation of various scenarios, enabling businesses to test their resilience to different types of disruptions and optimize their response strategies. Consider, for instance, a company using a digital twin to simulate the impact of a port closure; the simulation would allow them to identify alternative routes and optimize logistics before the actual event occurs.
Best Practices for Implementing Robust Risk Management Strategies
Implementing a robust risk management strategy within a digitally transformed supply chain requires a multi-faceted approach. Firstly, it’s crucial to establish a clear risk assessment framework that identifies potential threats and their likelihood and impact. This framework should be regularly reviewed and updated to reflect changes in the business environment. Secondly, businesses should invest in the right technologies and infrastructure to support real-time monitoring and data analysis.
This includes implementing appropriate cybersecurity measures to protect sensitive data. Thirdly, collaborative platforms that facilitate seamless information sharing between supply chain partners are essential. This enhanced collaboration fosters greater transparency and trust, leading to quicker responses to disruptions. Finally, regular training and education for employees are crucial to ensure that they are equipped to use the new technologies effectively and understand their role in the overall risk management strategy.
A well-defined incident response plan, regularly tested and updated, is also critical for minimizing the impact of any disruptions that may occur.
The Future of Digital Transformation in Supply Chains
The digital transformation of supply chains is far from over; it’s an ongoing evolution driven by technological advancements and evolving business needs. We can expect increasingly sophisticated and integrated systems, blurring the lines between physical and digital operations, leading to greater efficiency, resilience, and responsiveness. This section explores the key trends shaping the future of supply chain digitalization.
Emerging technologies are poised to revolutionize supply chain management in the coming years. The convergence of several technologies will create unprecedented opportunities for optimization and innovation, impacting everything from inventory management to logistics and customer service.
Impact of Emerging Technologies
The integration of 5G networks will significantly improve real-time data transmission and communication within the supply chain. This faster, more reliable connectivity will enable the use of IoT devices to monitor shipments, track assets, and optimize logistics in real-time, leading to reduced delays and improved efficiency. For example, a fleet of autonomous trucks equipped with 5G connectivity could share real-time traffic and road condition data, allowing for dynamic route optimization and reduced fuel consumption.
Furthermore, the potential of quantum computing, while still in its early stages, offers the prospect of solving complex optimization problems, such as route planning and demand forecasting, with significantly greater speed and accuracy than current classical computing methods. Imagine a scenario where a quantum computer can optimize the delivery routes for thousands of packages across a vast geographical area in a fraction of the time it currently takes, leading to significant cost savings and improved delivery times.
Autonomous and Self-Managing Supply Chains
The ultimate goal for many supply chain leaders is to create a fully autonomous and self-managing supply chain. This vision involves leveraging AI, machine learning, and advanced automation to minimize human intervention in various aspects of the supply chain. While complete autonomy is still some way off, significant strides are being made. For instance, automated warehouses using robots for picking, packing, and sorting are becoming increasingly common.
Similarly, autonomous vehicles are being tested for last-mile delivery and transportation of goods. These technologies, combined with advanced predictive analytics, will enable the supply chain to anticipate disruptions, proactively adjust to changing conditions, and optimize its operations continuously without significant human oversight. Consider a scenario where AI-powered systems automatically adjust inventory levels based on real-time demand fluctuations, preventing stockouts and minimizing waste.
This level of automation requires robust data security and reliable systems to ensure the integrity and efficiency of the entire operation.
Understanding the Supply Chain
A modern supply chain is a complex network of interconnected businesses, processes, and information flows working together to deliver goods and services from origin to end consumer. Its effectiveness significantly impacts a company’s profitability, competitiveness, and overall success. Understanding its components and the roles of various stakeholders is crucial for optimizing performance and navigating the challenges of today’s dynamic market.The modern supply chain encompasses a wide array of activities, from raw material sourcing and production to distribution, logistics, and ultimately, customer service.
These activities are interconnected and interdependent, meaning a disruption in one area can have cascading effects throughout the entire system. Efficient management requires careful coordination and collaboration across all stages.
Components and Functions of a Modern Supply Chain
A modern supply chain typically involves several key components, each with specific functions. These components work together seamlessly to ensure the efficient flow of goods and information. Failure in any single component can create bottlenecks and delays.
- Sourcing and Procurement: This involves identifying and selecting suppliers, negotiating contracts, and managing the procurement of raw materials and components. Effective sourcing ensures the availability of high-quality materials at competitive prices.
- Production and Manufacturing: This stage focuses on transforming raw materials into finished goods. Efficient production processes are crucial for minimizing costs and maximizing output.
- Inventory Management: This involves controlling the flow of goods throughout the supply chain, ensuring that sufficient inventory is available to meet demand without excessive storage costs. Techniques like Just-in-Time (JIT) inventory management aim to optimize inventory levels.
- Logistics and Distribution: This encompasses the movement of goods from production facilities to warehouses and ultimately to customers. This involves transportation, warehousing, and order fulfillment.
- Customer Service: This is the final stage of the supply chain, focusing on addressing customer inquiries, handling returns, and providing post-sales support. Excellent customer service enhances brand loyalty and repeat business.
Key Stakeholders in a Typical Supply Chain
Numerous stakeholders are involved in a typical supply chain, each playing a critical role in the overall process. Effective communication and collaboration among these stakeholders are essential for successful supply chain management.
- Suppliers: Provide raw materials, components, or services needed for production.
- Manufacturers: Transform raw materials into finished goods.
- Distributors: Transport and store goods before they reach retailers or customers.
- Retailers: Sell finished goods to end consumers.
- Customers: The ultimate recipients of the goods or services.
- Logistics Providers: Manage the transportation and warehousing of goods.
- Technology Providers: Offer software and hardware solutions for supply chain management.
Importance of Effective Supply Chain Management for Business Success
Effective supply chain management is no longer a mere operational function; it’s a strategic imperative for achieving sustainable business success. Companies with well-managed supply chains gain a competitive advantage in several ways.Effective supply chain management leads to reduced costs through optimized inventory levels, efficient logistics, and streamlined processes. It also improves responsiveness to market demands, enabling faster delivery times and improved customer satisfaction.
Furthermore, a robust supply chain enhances resilience against disruptions, mitigating risks associated with unforeseen events like natural disasters or geopolitical instability. Finally, effective management fosters better relationships with suppliers and customers, leading to stronger partnerships and increased profitability. Consider, for instance, how companies like Amazon have leveraged sophisticated supply chain management to achieve market dominance through speed, efficiency, and customer focus.
In conclusion, the digital transformation of supply chains is not merely a technological upgrade; it’s a strategic imperative for businesses aiming to thrive in today’s dynamic global marketplace. By embracing technologies like AI, IoT, and blockchain, organizations can achieve unprecedented levels of efficiency, transparency, and resilience. While challenges exist, the potential rewards—from reduced costs and improved customer satisfaction to enhanced risk management and sustainable practices—make the investment in digital transformation a crucial step towards long-term success.
The future of supply chain management is undeniably digital, and those who embrace this change will be best positioned to lead the way.
FAQ Insights
What is the ROI of digital transformation in supply chain?
The ROI varies greatly depending on the specific technologies implemented and the scale of the transformation. However, common benefits include reduced operational costs, improved inventory management, increased efficiency, and enhanced customer satisfaction, all leading to improved profitability.
How long does it take to implement digital transformation in a supply chain?
Implementation timelines depend on the complexity of the supply chain, the chosen technologies, and the organization’s resources. Projects can range from several months to several years.
What are the biggest hurdles to overcome when implementing digital transformation in supply chain?
Major hurdles include integration challenges with legacy systems, resistance to change within the organization, lack of skilled personnel, and high initial investment costs.
What is the role of cybersecurity in a digitally transformed supply chain?
Cybersecurity is paramount. Increased connectivity exposes the supply chain to greater cyber risks. Robust security measures, including data encryption, access controls, and regular security audits, are crucial to protect sensitive data and maintain operational integrity.





